The 500kg continuous furnace could become the dividing line between vertical and horizontal continuous furnaces. There are several reasons for this:
Limitations of Vertical Furnaces with Larger Capacities
Vertical furnaces are not suitable for large capacities. If the upper chamber (the melting chamber) becomes too large, it creates an unbalanced design. This top-heavy structure affects the stability of the furnace. Therefore, vertical furnaces are usually limited in size, particularly above the 500kg capacity.
Magnetic Circuit Design and Coil Size
Vertical furnaces use coils without magnetic yokes. This design limits coil size. Larger coils without magnetic yokes experience significant magnetic flux leakage, reducing electrical efficiency. For furnaces above 500kg, coils are typically designed with magnetic yokes to improve efficiency. However, vertical furnaces under 500kg maintain the advantage of a smaller, more cost-effective design.
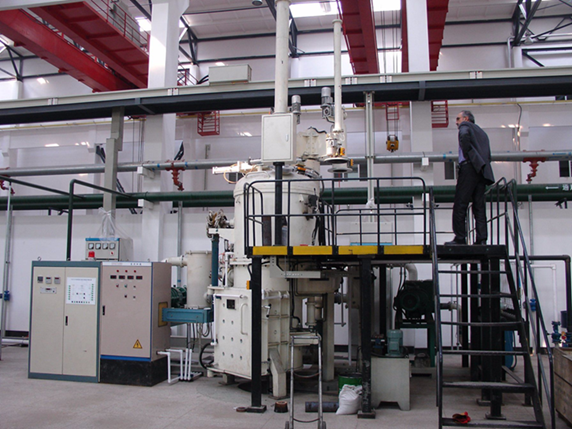

Application and Alloy Production Needs
Furnaces in the 500kg range are mostly used for producing master alloy ingots, usually around 80mm in diameter. These furnaces are not ideal for producing electrode rods. Electrode rods require larger diameters to match processes like electroslag remelting (ESR) or vacuum arc remelting (VAR). When the diameter increases, the length of the alloy produced decreases for the same furnace capacity. Therefore, vertical furnaces are better suited for small-batch production or high-value master alloys.
Usability and Maintenance Advantages
Vertical continuous furnaces offer significant advantages in usability and maintenance. They are simpler to operate and maintain compared to large horizontal furnaces. Their compact design makes them easier to manage, especially for companies with smaller-scale production or specialized alloys.
Domestic vs. International Market Trends
In China, several companies manufacture vertical continuous furnaces, especially in the 500kg and smaller capacity range. However, only a few international companies focus on vertical furnaces as their main product. ALD, a German company, stands out for producing high-performance vertical continuous furnaces. Other leading international manufacturers focus on larger horizontal furnaces. This suggests that the domestic Chinese market is still growing and has a strong demand for smaller vertical furnaces.
Conclusion
The 500kg continuous vacuum induction furnace serves as a key threshold between vertical and horizontal furnace designs. Vertical furnaces provide clear benefits for smaller capacities. They offer cost efficiency, better electrical performance, and easier maintenance. However, for larger capacities, horizontal furnaces tend to dominate. In China, vertical furnaces continue to be in high demand, particularly for small-to-medium-scale alloy production. As the market matures, the demand for these smaller furnaces will likely remain strong, making them a key component in the future of continuous melting technology.