In modern industrial manufacturing, welding technology is widely applied in metal processing, electronic devices, automobile manufacturing, aerospace, and many other fields. As a common joining method, brazing has become an essential tool for connecting metals. However, with continuous advancements in technology, vacuum brazing furnaces have gradually replaced traditional brazing furnaces in high-end manufacturing industries. So, what are the differences between vacuum brazing furnaces and traditional brazing furnaces? Why are more and more companies opting for vacuum brazing technology? This article will provide answers to these questions. Vacuum VS Tranditional Brazing Furnace
1. Working Principle and Limitations of Traditional Brazing Furnaces
Traditional brazing furnaces typically rely on heating and brazing flux to complete the metal joints. During brazing, metal parts are heated to a specific temperature, and the brazing filler metal melts to fill the joint, ultimately achieving a bond. The flux used in traditional brazing furnaces usually contains chemicals such as chlorides or fluorides, which help remove oxides from the metal surface and promote the bonding between the base metal and the filler.
Although traditional brazing furnaces have provided essential welding functions for several decades, they have certain limitations. First, while flux can remove oxides, the cleaning process after brazing is tedious. Unremoved flux residue can lead to corrosion and oxidation. Secondly, the working environment in traditional brazing furnaces is not ideal. External oxygen and moisture can interfere with the brazing process, leading to joints with inadequate strength. Finally, traditional brazing furnaces have lower precision in temperature and pressure control, which can result in unstable welding quality.
2. Advantages of Vacuum Brazing Furnaces
Compared to traditional brazing furnaces, vacuum brazing furnaces use more precise and stable brazing technology. The key feature of vacuum brazing furnaces is their ability to operate in a high vacuum environment, eliminating the impact of oxygen and moisture on the brazing process. Below, we will analyze the advantages of vacuum brazing furnaces.
1. No Flux, No Pollution
One of the greatest advantages of a vacuum brazing furnace is that it does not require flux. In traditional brazing, while flux helps remove oxides, it also brings problems such as the need for cleaning and the potential for corrosion. Vacuum brazing furnaces create a high vacuum environment that prevents oxidation of the metal surface, eliminating the issue of flux residue. The absence of flux not only reduces pollution during the manufacturing process but also significantly improves product quality and durability.
2. High-Precision Temperature and Pressure Control
Vacuum brazing furnaces operate with high precision in temperature and pressure control. This allows for better stability in the welded joints. In a vacuum environment, oxidation layers are prevented, ensuring better wetting and flow of the brazing filler metal. Consequently, the brazed joints are more reliable in terms of strength, and the appearance is also improved. This precise control makes vacuum brazing ideal for high-precision applications, such as aerospace, electronics manufacturing, and automotive industries.
3. Excellent Brazing Quality
Because vacuum brazing furnaces use advanced vacuum technology and precise temperature control, the brazing process is not interfered with by the surrounding environment. This results in reduced oxidation and better wetting of the filler metal. As a result, the brazed joints are not only stronger but also more visually appealing. This is especially important in fields requiring high precision, such as aerospace, electronics, and automotive manufacturing, where vacuum brazing provides a clear advantage.
4. Energy Efficiency and Environmental Protection
Vacuum brazing furnaces are more energy-efficient than traditional brazing furnaces. Traditional brazing furnaces typically consume more power due to less precise temperature control, leading to energy waste. In contrast, vacuum brazing furnaces use intelligent control systems to reduce energy consumption. This not only helps save production costs but also reduces the environmental impact.
5. Increased Production Efficiency
In traditional brazing furnaces, the use of flux requires additional cleaning and post-treatment steps. Vacuum brazing furnaces, however, eliminate the need for flux, reducing the number of cleaning processes. This leads to higher production efficiency. Furthermore, vacuum brazing furnaces are highly automated, making the operation simpler and reducing human error, which further enhances production efficiency.
3. Vacuum VS Tranditional Brazing Furnace
| Item | Traditional Brazing Furnace | Vacuum Brazing Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Brazing Environment | Normal air environment, susceptible to oxygen and moisture | High vacuum environment, prevents oxidation and contamination |
| Flux Use | Requires flux, cleaning is troublesome | No flux required, no residue pollution |
| Brazing Quality | Unstable quality, defects such as porosity and slag | High-quality, dense joints with no defects |
| Temperature Control | Low precision, temperature variations | Precise temperature control system |
| Production Efficiency | Cleaning after brazing, lower efficiency | High efficiency with fewer cleaning steps |
| Environmental Impact | Flux and residue contribute to pollution | No flux, environmentally friendly |
| Energy Efficiency | High energy consumption, inefficient | Energy-efficient, lower production costs |
4. Vacuum VS Tranditional Brazing Furnace Conclusion
As manufacturing industries demand higher product quality, vacuum brazing furnaces, with their efficient, precise, and environmentally friendly features, are gradually becoming the industry standard. While traditional brazing furnaces still hold value in certain applications, vacuum brazing furnaces offer a more ideal solution for high-end manufacturing and precision brazing needs.
For companies looking for high-quality, low-cost, and efficient production, vacuum brazing furnaces are undoubtedly the right choice for future development. Understanding the differences between vacuum and traditional brazing furnaces will help businesses make informed decisions, increase overall productivity, and meet the increasingly stringent market requirements.
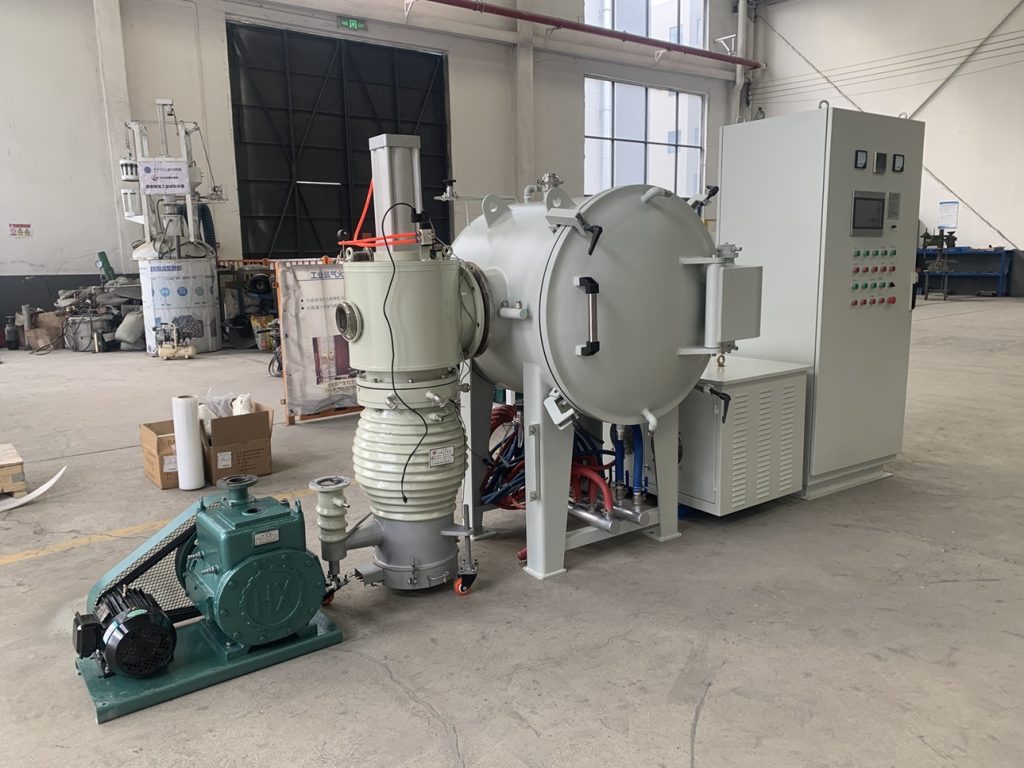
Vacuum Brazing Furnace
A molybdenum strip vacuum brazing furnace is a specially designed equipment used for brazing in high-temperature vacuum environments, utilizing molybdenum as the main heating element or structural material. This equipment is widely used for welding high-melting-point materials, high-temperature alloys, and dissimilar materials due to its excellent high-temperature performance and vacuum compatibility.
For more details on the vacuum brazing furnace, please click on the image link for the molybdenum strip vacuum brazing furnace.